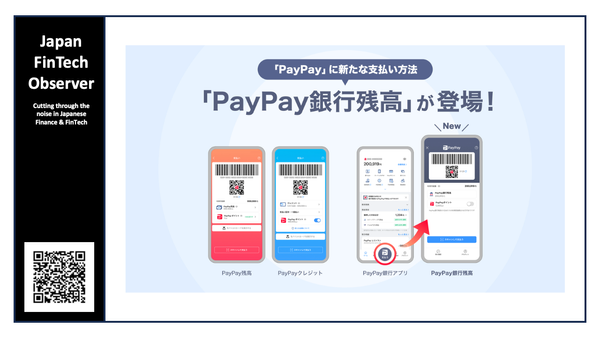
The third meeting of the Financial System Council’s “Working Group on Fund Settlement Systems”
The third meeting of the Financial System Council’s “Working Group on Fund Settlement Systems” was held on Thursday, October 24, 2024. As…

The third meeting of the Financial System Council’s “Working Group on Fund Settlement Systems” was held on Thursday, October 24, 2024. As is customary, the secretariat provided explanatory materials which outline the background, discussion points, and reference materials for the working group.
In addition, the meeting materials include a discussion document by MUFG on the foreign currency funding needs for corporations.
1. Secretariat’s explanation
The secretariat’s explanatory materials specifically tackle the regulation of “advancement services” and the participation of foreign financial institutions in syndicated loans.
1.1 Regulatory approach to advancement services:
The secretariat delves into the complexities of regulating advancement services in Japan. It highlights the challenges posed by diverse legal frameworks and the need for clear regulatory boundaries.
Background and Definition
Advancement services are financial services where a business provides funds to a user upon request and later collects the advanced amount from the user. However, these services fall outside the typical scope of the Money Lending Business Act and the Payment Services Act, requiring a case-by-case determination of their legal status.
Challenges and Opinions
Several challenges in regulating these services were identified:
- Complex Legal Structure: Existing laws are not tailored for these services, making it difficult to establish clear regulatory boundaries.
- Functional Similarity Across Different Legal Structures: Services with similar economic outcomes can be structured under various legal frameworks, potentially leading to regulatory loopholes.
- Need for Cross-sectional and Functional Regulation: The need for comprehensive regulation covering diverse legal structures and ensuring consumer protection is emphasized.
- Possibility of Categorizing Businesses: Similar to financial instruments businesses, categorizing these businesses and adjusting the Money Lending Business Act accordingly is suggested.
- Necessity of Practical Research: Conducting thorough research on existing services, their necessity for regulation, and their compatibility with existing legal frameworks is deemed essential.
- Addressing Concerns Related to BNPL: Concerns raised about “Buy Now Pay Later” (BNPL) services, especially their potential to enable over-borrowing and fraudulent activities, require careful consideration.
Past Consultation Cases and Interpretations
The secretariat presents two previous cases where the Financial Services Agency (FSA) addressed the legality of specific advancement services:
- Case 1: Payroll Advance Service (Response published on December 20, 2018): This case involved a service where employees received a portion of their salary in advance, deducted from their actual salary later. FSA deemed it outside the scope of the Money Lending Business Act, citing that it functioned as a short-term advance on wages.
- Case 2: Medical Expense Advance Collection Service for Educational Institutions (Response published on December 25, 2019): This service involved advancing medical expenses for students during school trips. FSA considered it outside the scope of the Money Lending Business Act, primarily because the service fee was nominal and not dependent on the user’s creditworthiness.
Advancement Services and the Money Lending Business Act
The secretariat focuses on the applicability of the Money Lending Business Act to advancement services. It explains the definition of “Loan” under the Act and analyzes its relevance to these services.
- Definition of “Loan”: The Money Lending Business Act defines a loan as “the lending of money or the intermediation of the borrowing and lending of money,” encompassing various methods achieving similar economic effects.
- Judicial Precedent: A judicial precedent states that a consumer loan is deemed to have been established if the borrower obtains the same economic benefit as if they had received actual funds. This suggests that some advancement services might fall under the Act’s purview.
Examples of Services with Advancement Elements
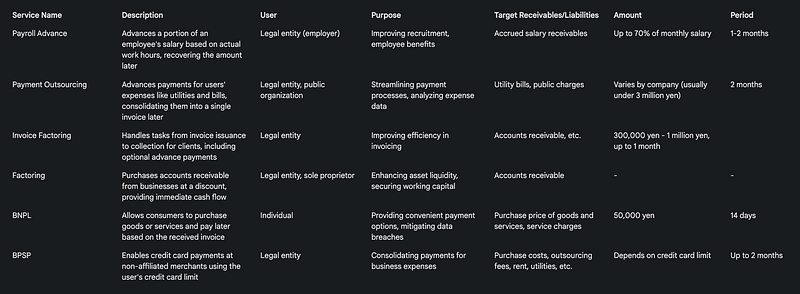
The secretariat provides above examples of services containing advancement elements, illustrating the diverse landscape.
1.2 Participation of Foreign Financial Institutions in Syndicated Loans
The secretariat discusses the challenges faced by foreign financial institutions when participating in syndicated loans arranged within Japan.
Current Situation and Challenges
While Japanese companies utilize foreign currency syndicated loans for overseas expansion, current regulations restrict the participation of some foreign financial institutions.
- Current Legal Framework: Foreign banks with branches in Japan can participate in syndicated loans. However, foreign financial institutions without such presence need to register as Money Lenders, requiring them to establish a physical presence and fulfill human resource requirements, which is often impractical.
- Impact on Japanese Companies: Japanese companies seeking local financing for overseas projects face limitations as some local banks might be unable to participate in the syndicated loan due to these regulatory hurdles.
Considerations for Regulatory Changes
The secretariat emphasizes the need to re-evaluate the regulatory framework governing the participation of foreign financial institutions in syndicated loans arranged within Japan. This re-evaluation should consider:
- User Protection: Ensuring the protection of borrowers, considering that foreign lenders might not be subject to the same level of supervision as domestic entities.
- Supervisory Effectiveness: Maintaining the effectiveness of regulatory oversight, even with the participation of foreign lenders.
- International Practices: Learning from best practices and regulatory approaches in other jurisdictions.
- Balance between Regulation and Market Needs: Finding the right balance between regulation and facilitating smooth access to financing for Japanese companies operating globally.
1.3 Points for Discussion
The secretariat summarizes the key discussion points for the working group meeting.
Advancement Services
- Developing a Judgement Framework: While acknowledging the need for case-by-case assessment, the group needs to establish a clear framework for determining the legal status of advancement services. This framework should consider factors like economic effects, creditworthiness assessment, and the need for consumer protection.
- Specific Considerations: The framework should address practical aspects like the length of the advancement period and potential disparities in fees based on creditworthiness.
Foreign Financial Institution Participation in Syndicated Loans
- Re-evaluating Regulatory Requirements: The working group needs to discuss the current requirements for foreign financial institutions to participate in syndicated loans arranged within Japan, considering their necessity and potential impact on Japanese companies seeking financing.
Overall, this document sets the stage for crucial discussions on the evolving landscape of financial services in Japan, focusing on striking a balance between promoting innovation, ensuring user protection, and maintaining a stable financial system.
2. Foreign currency funding needs of corporations — MUFG
MUFG has provided a discussion document about syndicate loans and their potential to meet the increasing foreign currency funding needs of Japanese companies expanding globally.
Current Challenges
- Japanese companies need more foreign currency funding due to global expansion (M&A, etc.).
- Japanese financial institutions have limited foreign currency lending capacity.
- Foreign financial institutions can’t easily lend within Japan due to regulations (Money Lending Business Act).
Proposed Solution
- Use syndicate loans to allow foreign financial institutions to participate in lending to Japanese companies.
- Syndicate loans: Multiple lenders provide a loan under a single contract, ensuring fairness and preventing individual lender dominance.
Benefits of Syndicate Loans
- For Japanese companies: Increased access to foreign currency funding at potentially better terms.
- For Japanese financial institutions: Opportunity to participate in larger deals and offer more comprehensive services to clients.
- For foreign financial institutions: Access to Japanese market without full regulatory registration.
Key Points:
- Foreign currency lending demand is expected to increase further.
- Syndicate loans offer a practical solution to address regulatory constraints while meeting market needs.
- MUFG presents data on M&A deals and syndicate loan usage, demonstrating the growing importance of this financing method.
Overall, the document advocates for a regulatory framework that enables foreign financial institutions to participate in syndicate loans, thereby supporting the growth and global expansion of Japanese businesses.
Please follow us to read more about Finance & FinTech in Japan, like hundreds of readers do every day. We invite you to also register for our short weekly digest, the “Japan FinTech Observer”, on Medium, on LinkedIn, or on Substack.
We also provide a daily short-form Japan FinTech Observer news podcast, available via its Podcast Page. Our global Finance & FinTech Podcast, “eXponential Finance” is available through its own LinkedIn newsletter, or via its Podcast Page.
Should you live in Tokyo, or just pass through, please also join our meetup. In any case, our YouTube channel and LinkedIn page are there for you as well.